Active safety
JARI, centering on its active safety group, analyzes causes of accidents in relation to human,
vehicle and road factors as part of its study on accident prevention measures and systems.
Currently JARI is engaged in the investigation of driver’s visual field and visibility, driving behavior,
accident generation mechanisms, driver support technology.
At a time when automatic emergency braking and other active safety technologies are being commercialized,
we need to examine the effectiveness of these technologies.
Accident generation mechanisms
Making use of accident statistics, accident on-site data and driving recorder data on near miss cases, JARI analyzes background factors and accident causing factors, and replicates typical accident and near miss scenes on the mock roads to examine accident generation mechanisms and to identify effective accident prevention measures.
Driver characteristics
We at JARI examine drivers’ behaviors in normal traffic situations and their abilities to avoid an accident at a sudden dangerous situation.
We attempt to classify driving action patterns of the elderly driver group which exhibits widening individual differences in driving ability.
Research into driver characteristics
Driving action is comprised of a chain reaction of recognition, judgment and operation. In the area of the driver’s recognition, for example, we investigate the visual search function, information processing abilities and risk avoidance operations of drivers.
Driver interface
Due to the increasing use of advance technologies in automobiles,
it has become possible to supply a greater amount of information to drivers.
JARI is accordingly researching appropriate methods of information supply, onboard image display,
warning functions which will ensure greater safety and greater convenience.

Experiment on onboard display assessment methods
Simulation of diverse running situations by a 360-degree spherical screen and a rocking device
In 2009 JARI acquired a new driving simulator to execute a great variety of experiments and assessment tests targeted primarily at active safety for the reduction of traffic accidents.
This simulator is equipped with a 360-degree spherical screen to show wide-angle video images and with a rock device consisting of a hexapod and turntable for the simulation of
realworld road running conditions.
The cabin, measuring instruments, software programs of the simulator are replaceable so as to suit diverse testing needs.

Omnidirectional-vision driving simulator
Specification
| Steering wheel | Accel/ brake pedals |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manipulative reaction system (AC servo motor drive) |
Steering wheel | Rated torque:10 Nm (instantaneous max value: 33 Nm) Rated angular velocity:3.4 rad/s (instantaneous max value: 17.9 rad/s) |
Accel/ brake pedals |
Rated thrust:480 N (instantaneous max value: 1,450N) Rated velocity:1 m/s (instantaneous max value: 1.5 m/s) |
| Screen | Projector | Full-perimeter video performance (measured values) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video display system |
Screen | Spherical screen:Diameter 8m Sight distance:Approx. 3.7m(eye-point height) Viewing angle:Horizontal 360°×Vertical 65° |
Projector | Full-perimeter video:Full-spec Hi-Visionprojector x 12 units Door mirror video:SXGA+ Projector × 2units (Rt, Lt) Room mirror video:WXGA Plazmadisplay×1unit |
Full-perimeter video performance (measured values) |
Image resolution:4.67 minute/OLP (eye point) Ave. brightness:53.3 cd/m2(amp power 70%) Ave. contrast ratio:8.86:1 |
| Movable range | Max speed/ angular velocity (instantaneous max value) |
Max acceleration/ angular accel. (instantaneous max value) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-axis rocking system | Movable range | X : ±300 mm ROLL : ±12° Y : ±300 mm PITCH : ±12° Z : ±300 mm YAW : ±12 ° |
Max speed/ angular velocity (instantaneous max value) |
X : ±700 mm/s ROLL : ±20°/s Y : ±700 mm/s PITCH : ±20°/s Z : ±600 mm/s YAW : ±20°/s |
Max acceleration/ angular accel. (instantaneous max value) |
X : ±0.4 G ROLL : ±110°/s2 Y : ±0.4 G PITCH : ±110°/s2 Z : ±0.4 G YAW : ±110°/s2 |
| Movable range | Max angular velocity (instantaneous max) |
Max angular acceleration (instantaneous max) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yaw rotation device | Movable range | ±300° | Max angular velocity (instantaneous max) |
±60°/s | Max angular acceleration (instantaneous max) |
±120°/s2 |
| Measuring/ recording equipment |
Video/audio data Cardiac, muscular, similar biosignals Data synchronization Contact/non-contact visual direction Driver manipulation amount, vehicle condition, manipulative reaction, etc |
|---|
Main research items
- Traffic accident generation mechanisms
- Driver distraction
- Driver assist systems, Human-machine interface
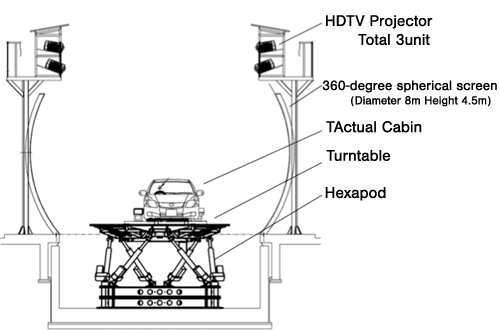
Profile of the omnidirectional-vision driving simulator
JARI’s omni-vision driving simulator shows the images of virtual traffic situations on its screen installed all around the cabin. The cabin itself can be rotated ±300 degrees so that it is possible to replicate a diversity of traffic situations on the screen (see Attachment-1). In comparison with JARI-ARV, the driver’s feeling of realistic driving is not so strong with this simulator. Nevertheless, the simulator gives greater freedom of condition setting such as the setting of dangerous situations and driver assist systems, thus making it easier and safer to assess the effectiveness of various measures and the effect on driving performance. Consequently it is possible to select typical danger scenes by using the omni-vision driving simulator and introduce these scenes into the JARI-ARV for the verification of actual driving characteristics.
JARI-ARV(augmented reality vehicles)
JARI has developed ARV, an augmented reality experiment vehicle that resembles a road running type driving simulator. Compared to the conventional indoor type driving simulators, JARI-ARV can replicate more accurately the realities leading to traffic accidents. Using this simulator vehicle, it has become possible to analyze accident causes from actual driving data and to verify the effectiveness of various accident prevention measures. In combination with the mock roads and the omnidirectional-vision driving simulator, JARI-ARV can be used in a wide variety of accident prevention studies.

JARI-ARV(augmented reality vehicles)
JARI-ARV profile
- JARI-ARV is a passenger car having on its hood a video camera and a large display showing the video images of the surroundings realtime. The subject is instructed to drive the simulator vehicle along the test course while watching the video images, in much the same way as he/she normally drives on the road (see Figure 2).
- The display system on the hood is capable of superposing virtual vehicles and pedestrians on the background scene of the mock road, thus reproducing dangerous situations such as sudden entry of a pedestrian or a vehicle into the driving scene from a blind corner.
- JARI-ARV allows any possible traffic scene to be added to the display scenario from a PC.

Forward display view seen from inside JARI-ARV
Combination with driving simulators and mock roads
-
Combination with driving simulators and mock roads
As shown in Reference-1, the omni-vision driving simulator permits many dangerous traffic situations to be programmed into its driving scenes, and replicates actual accident situations on the screen. But since the conventional simulators are used in indoor settings without actual on-road driving operation, it has been difficult for those simulators to obtain realistic driver actions and vehicle behaviors. - The mock roads, reproducing the typical structures of city roads, make up a unique test course at JARI (see Reference-2), which enables replication experiments on dangerous scenes. With the mock roads, however, it is not possible to reproduce dangerous situations involving human beings while only a limited number of traffic situations can be added to the replication experiments.
- On the other hand, JARI-ARV incorporates the advantages of both driving simulators and mock roads – the first advantage being the reproduction of wide-ranging accident scenes and the second advantage being experimentation in the actual running environment. Consequently it is possible to apply JARI-ARV to a variety of active safety studies including the analysis of accident generation mechanisms and the development of accident prevention systems.

Characteristic of the JARI-ARV
Examples of JARI-ARV usage
As for JARI-ARV, the following utilization is expected.
-
Analysis of accident generation mechanisms
Through driving tests on a test course with replicated dangerous traffic scenes, accident causing factors such as human error can be analyzed. -
Support for driver assist system development
JARI analyzes running data that are linked to accidents or dangerous situations so as to determine the driver’s characteristic actions and vehicle behaviors. We hope to obtain suitable driver assist methods and assess the effectiveness of warning and other accident avoidance measures. -
Safe driving experience tools
JARI makes use of various tools for professional, elderly and other drivers to experience mock accidents and dangerous traffic situations.
Example of use in accident generation mechanism study
-
Right-turn accident at an intersection
-
A vehicle-pedestrian accident
※3D computer-graphic images of a vehicle and a pedestrian
